10 Abdomen Scan
10.1 Overview
10.1.1 Terminology
U/S Whole Abdomen= All abdominal organsU/S Upper Abdomen= All abdominal organs - (Bladder & Reproductive orgs)U/S KUB= Kidneys + Bladder + Reproductive orgs
10.1.2 Echogenicity
Relative echogenicity on ultrasound (high to low):
Darling Parents So Love Kids
(Ref: radiopedia)
10.2 Liver
10.2.1 Overview
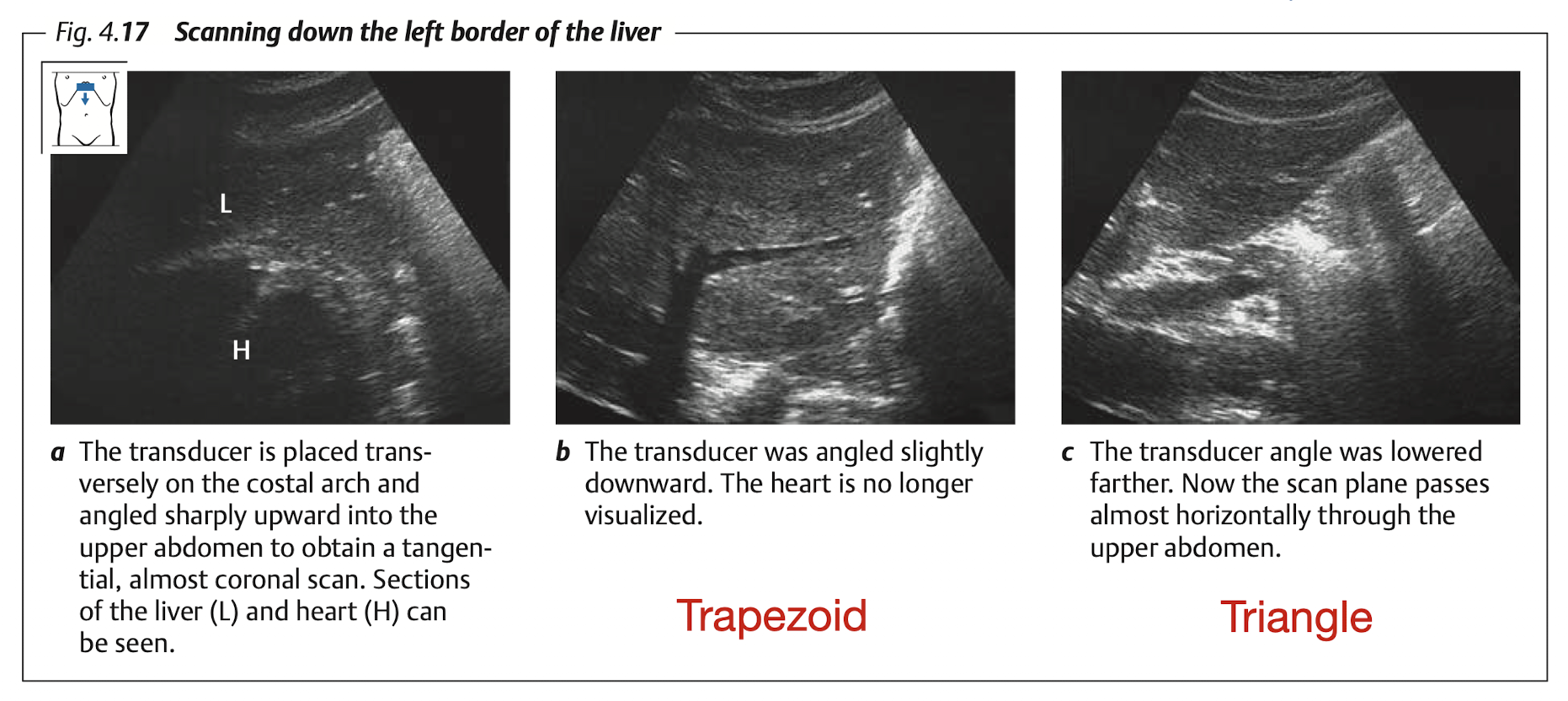
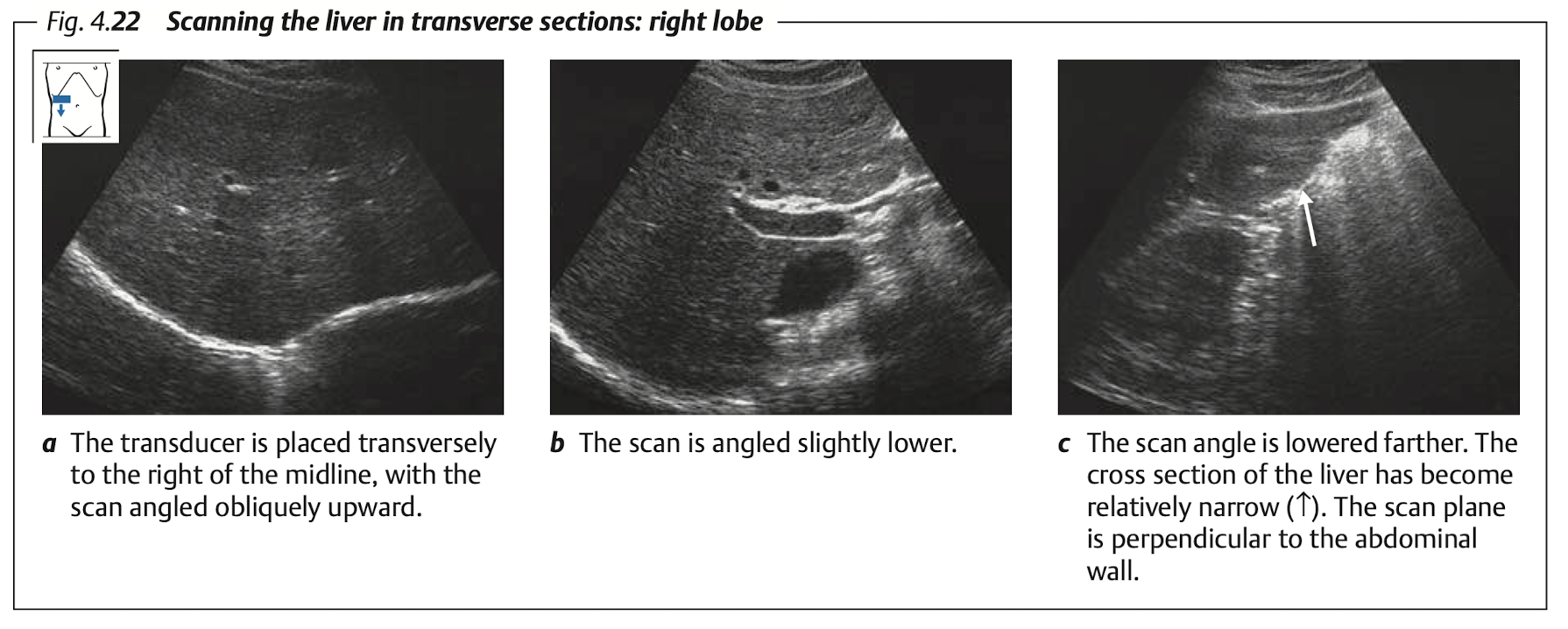
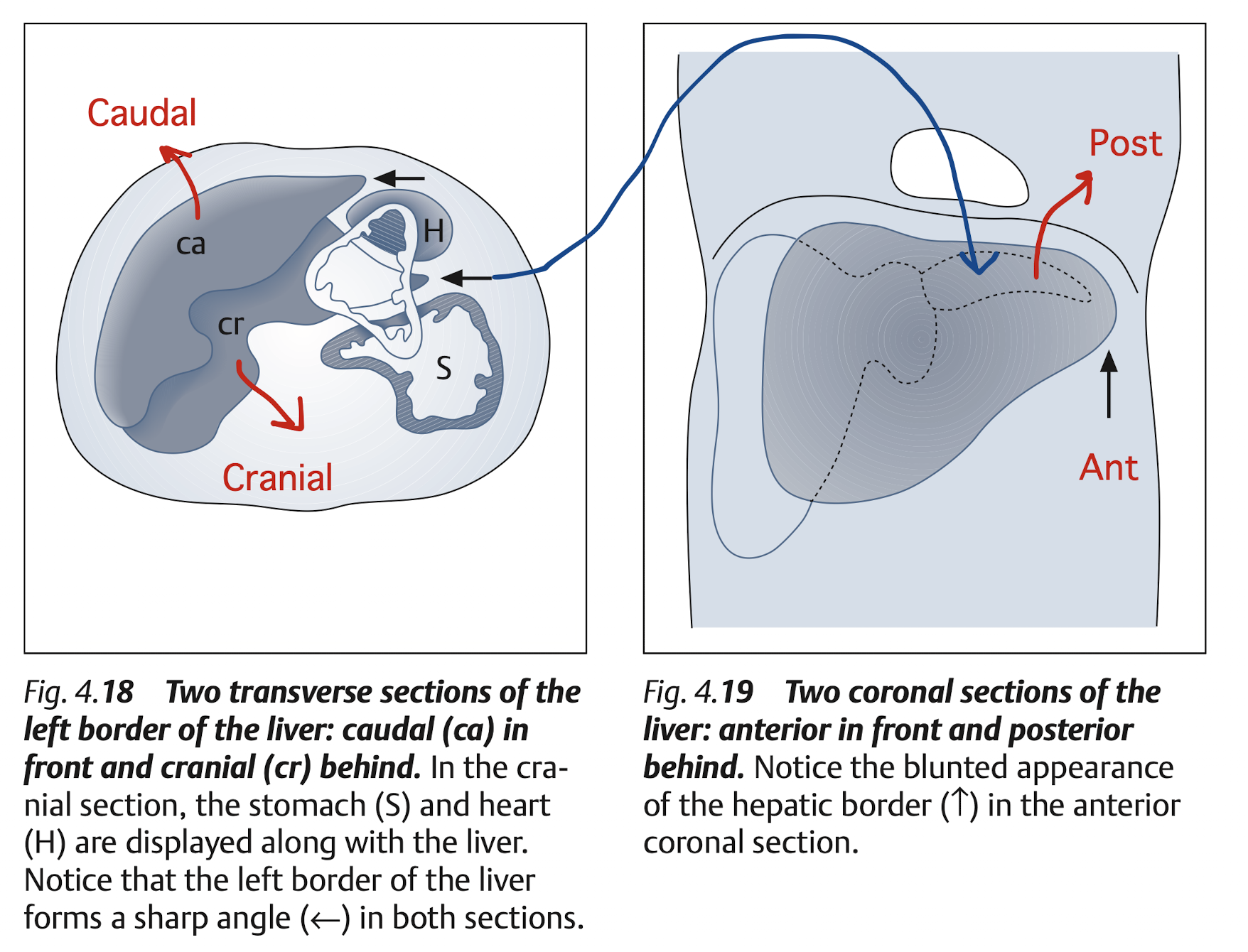
Subcostal: Transverse & longitudinal view of RL & LL (LL must includes caudate lobe)
Intercostal: RL
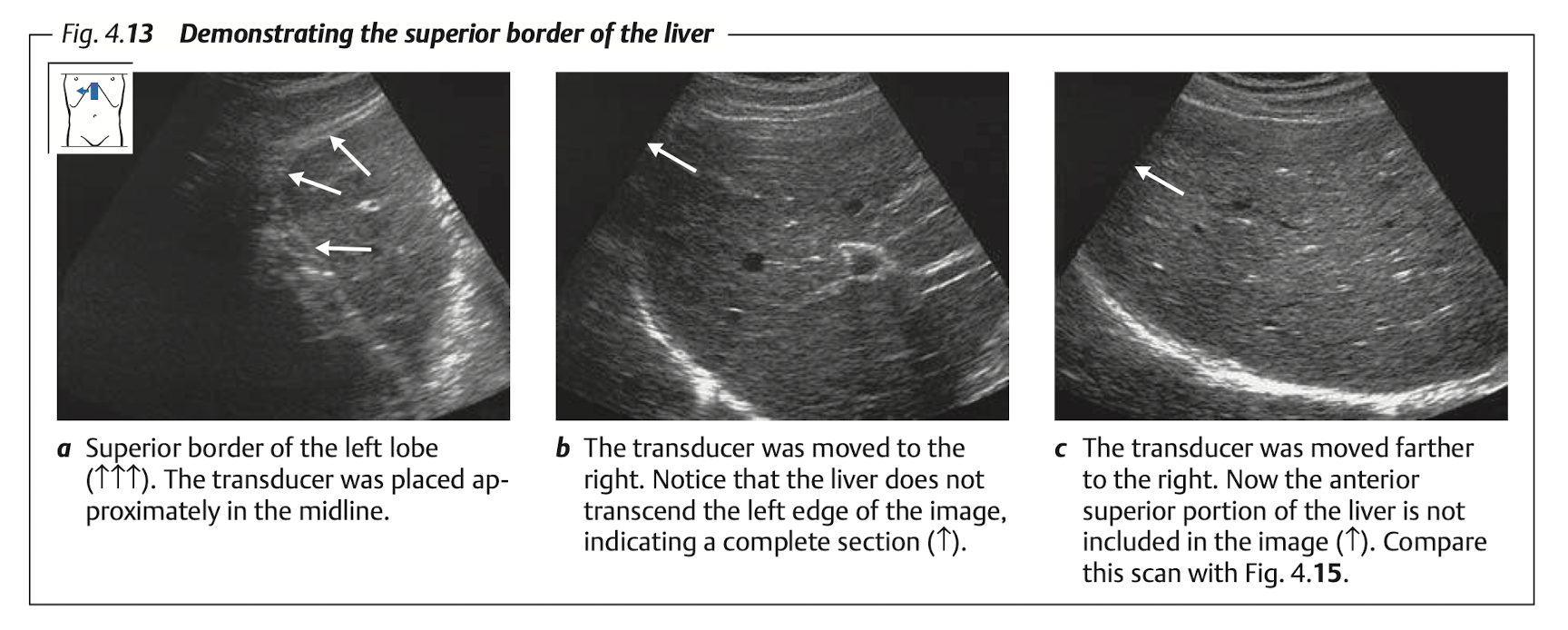
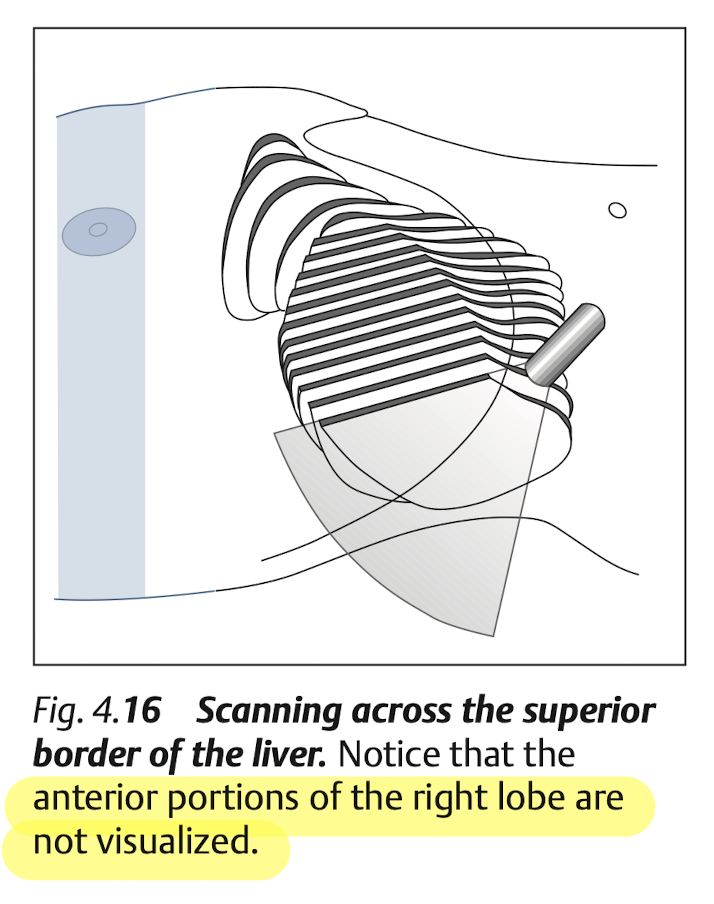
Blind spot of liver at “superior portion of Rt lobe”
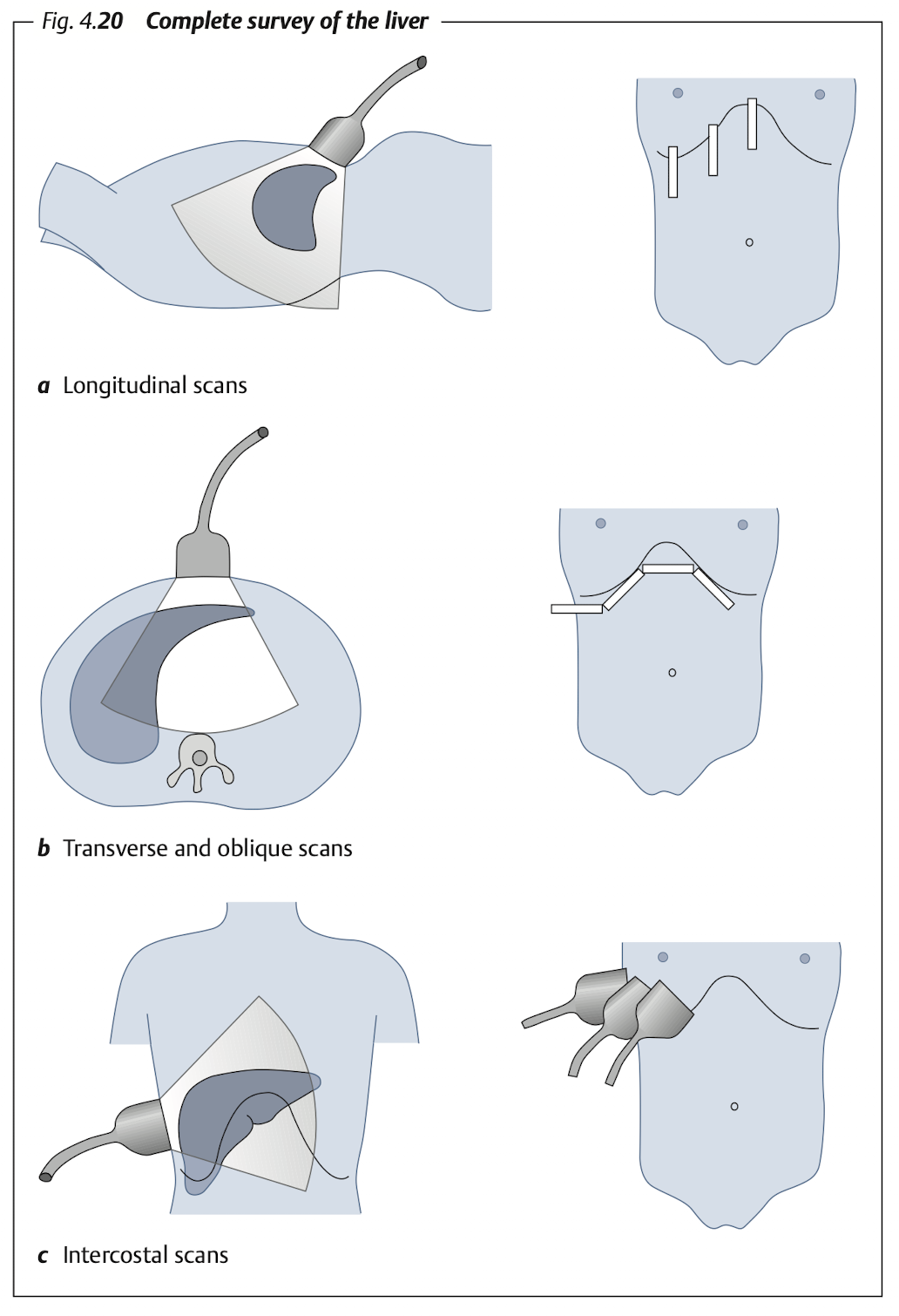
10.2.2 Measure
Normal liver span:
15 - 17 cm(sagital, at MCL)Enlarge:
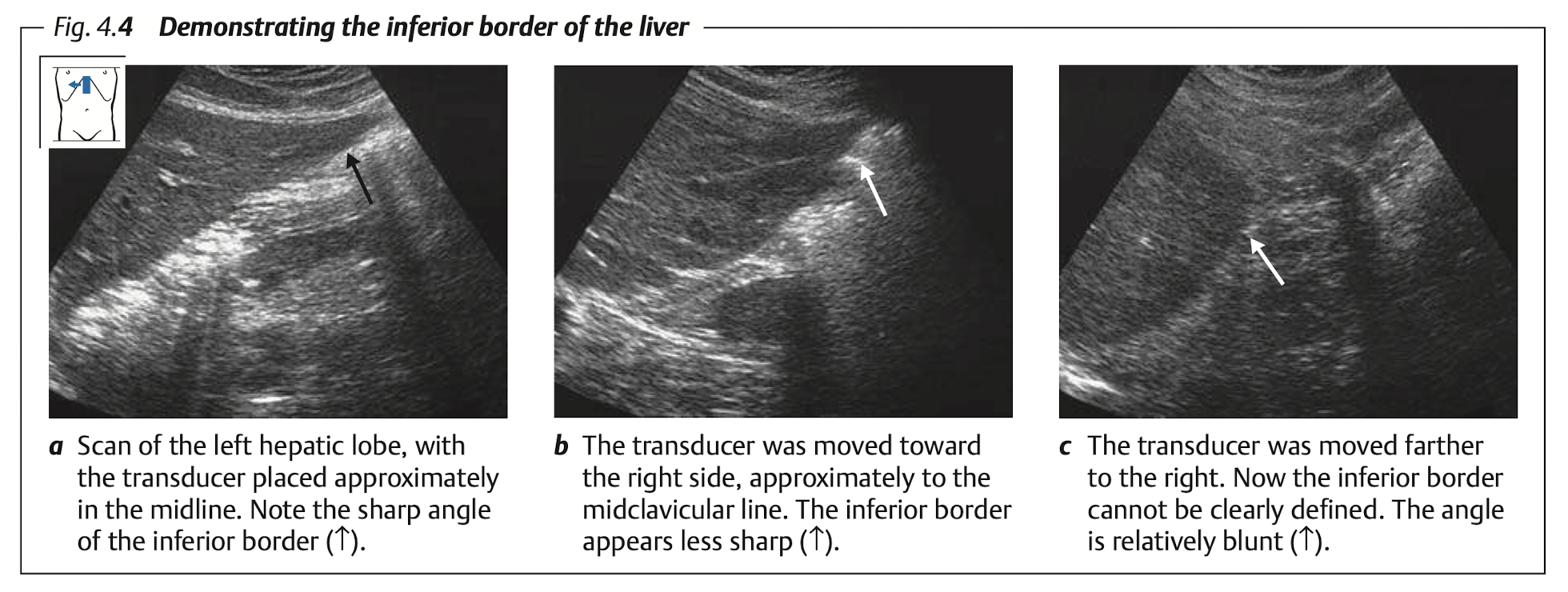
> 15.5 cmHepatomegaly: confident if liver extend to caudal of Rt kidney
(Ref from [2])
10.2.3 View: Longitudinal
10.2.4 View: Transverse
10.3 Gallbladder
View: transverse & longitudinal
Measure:
- Diameter: long (9 -
11cm), TV (< 4cm) - Wall thickness at anterior wall in TV section (
< 3mm)
- Diameter: long (9 -
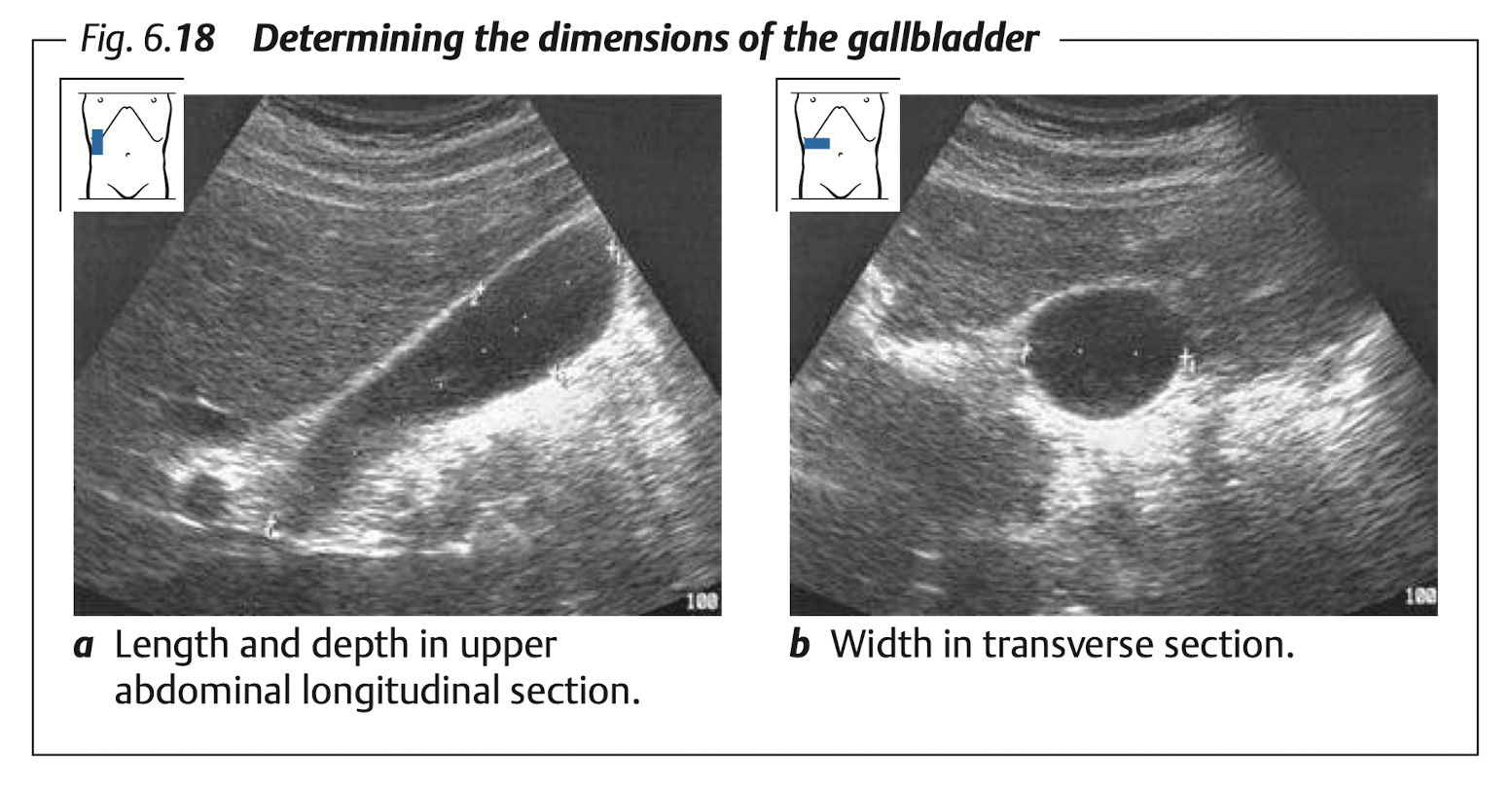
10.4 Porta Hepatis
10.4.1 Measure: CBD & PV
CBD
- Measure: internal diameter
< 0.6cm (< 0.9for post-cholecystectomy)- Age > 60 yrs can dilate 0.1 cm / 10 yrs
PV
- Measure: internal diameter
< 13mm - Flow direction:
hepatopetal? (toward liver) orhepatofugal? (away from liver)
10.4.2 View: CBD & PV
View: longitudinal scan (with lt lateral decubitus) to see porta hepatis Figure 10.10
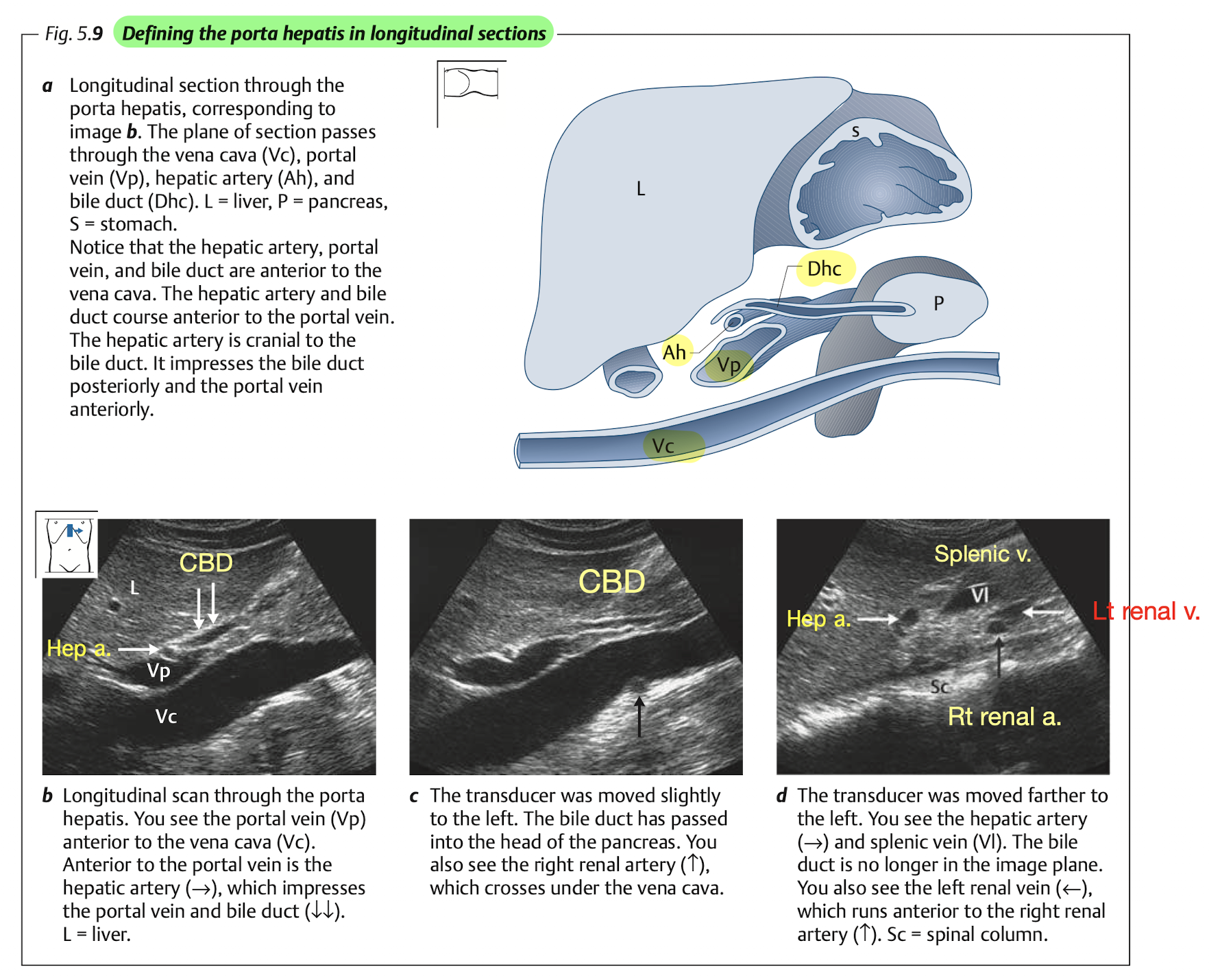
Tips: identifying CBD
- CBD will appear anterior and parellel to PV and IVC.
- Color doppler will show no flow at CBD.
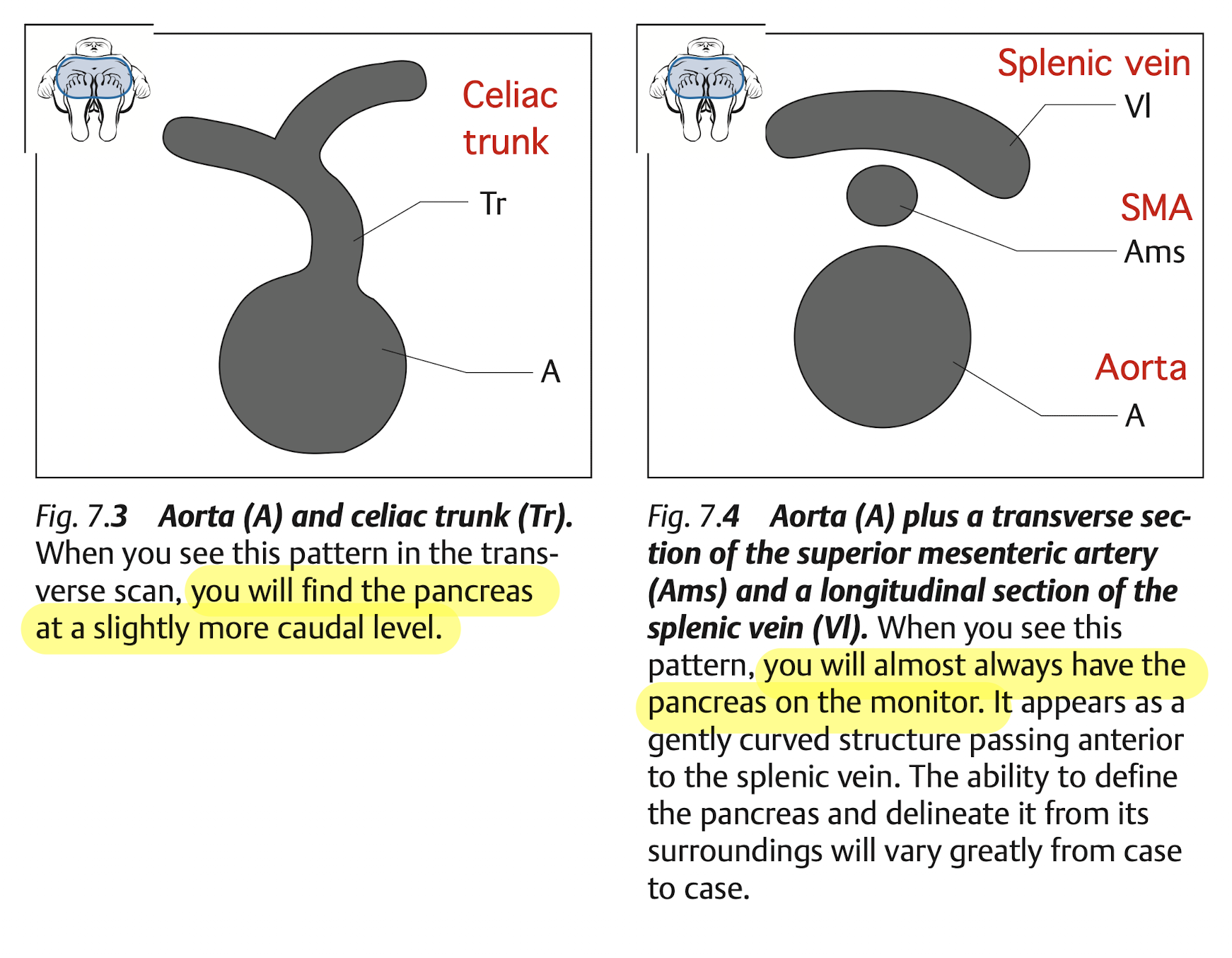
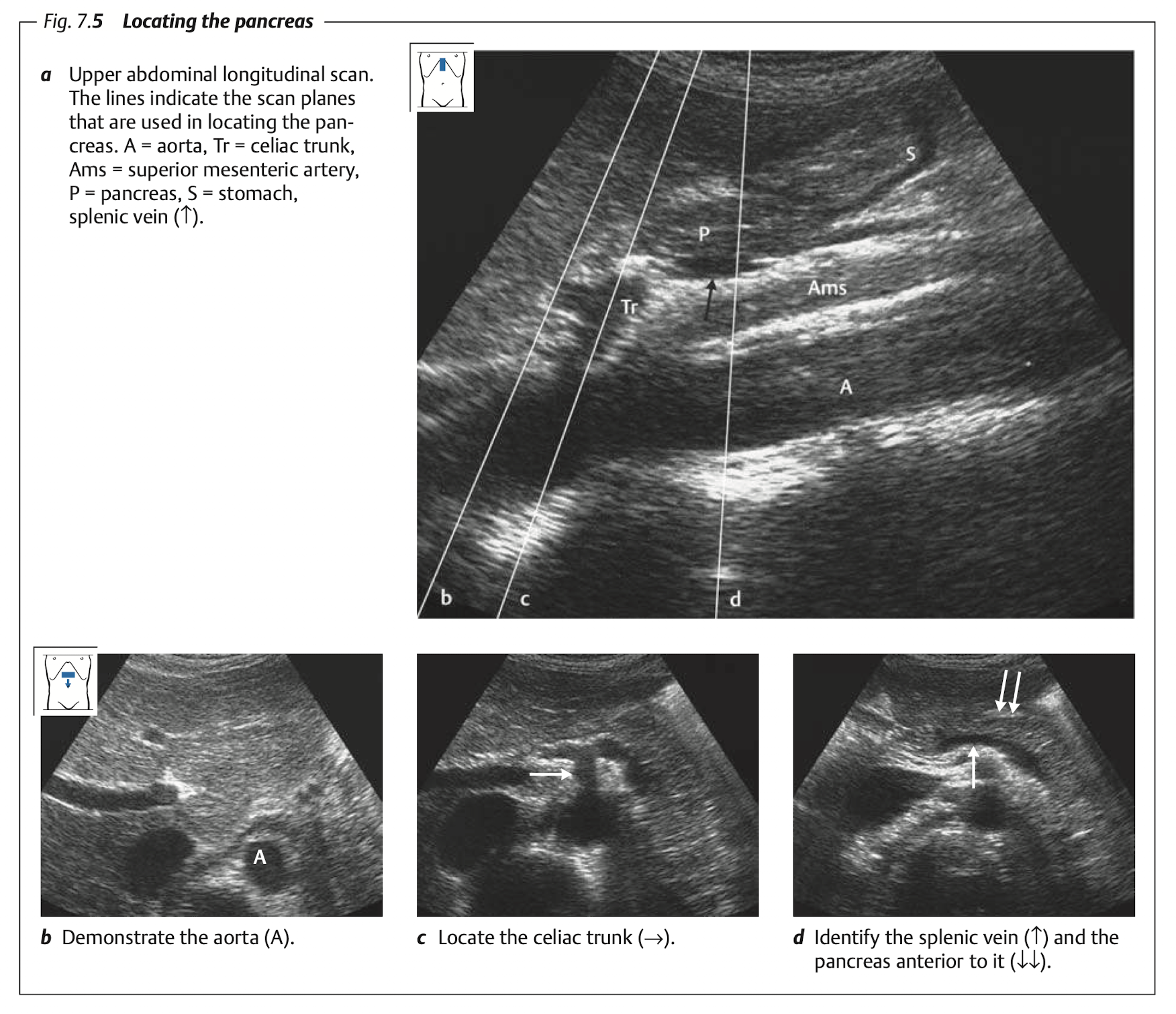
10.5 Pancreas
10.5.1 View
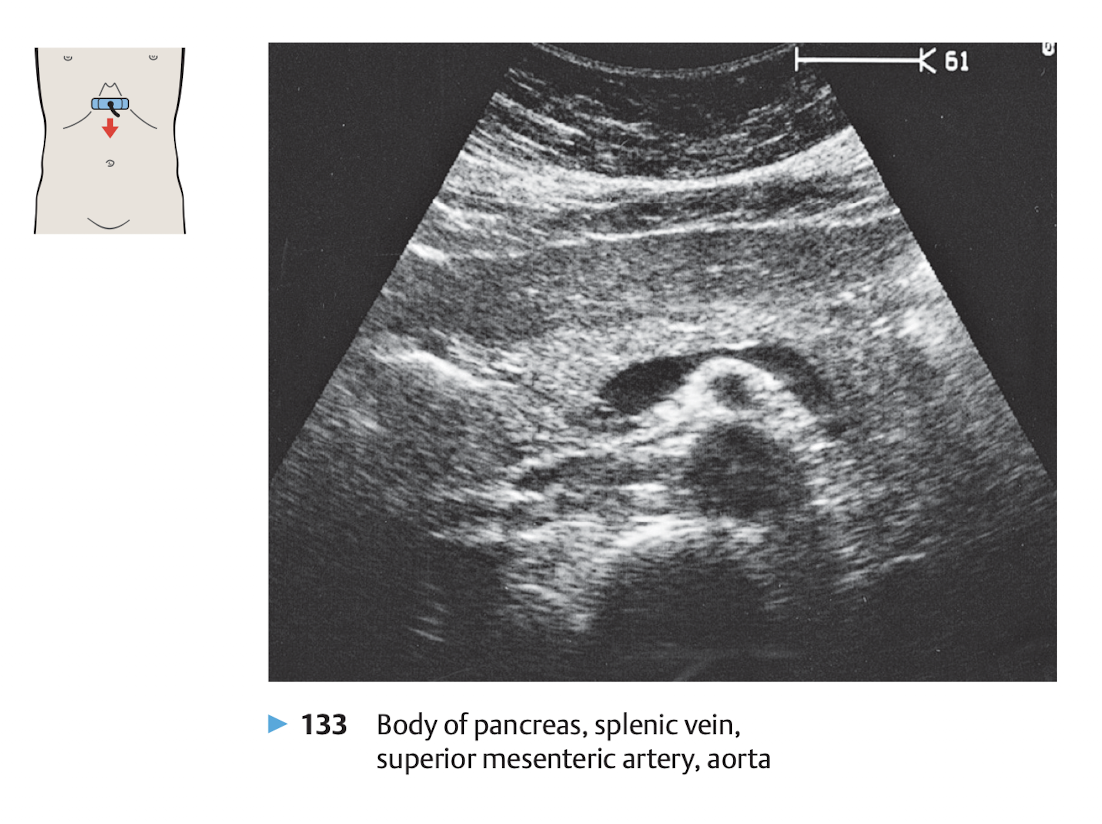
View: transverse view, angle the probe slightly upward to the liver.
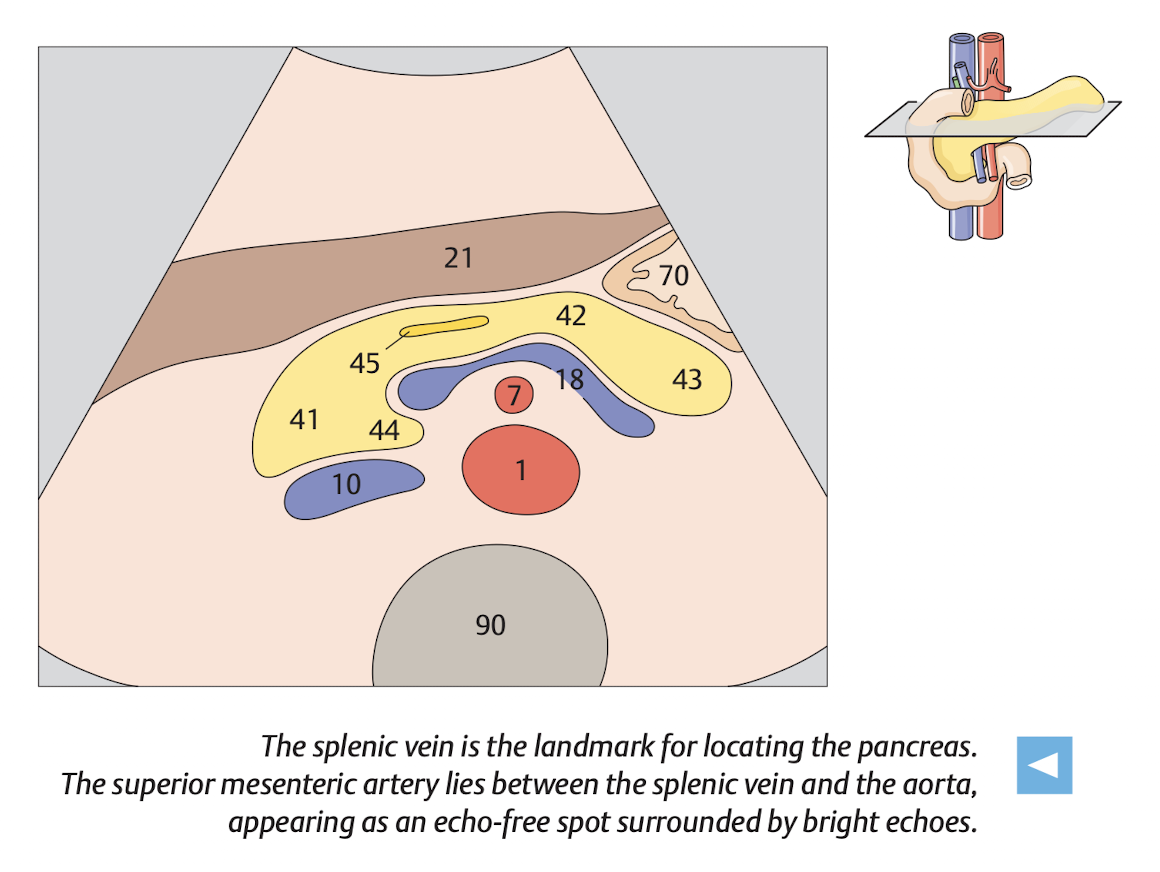
use splenic vein as a land mark
The money shot of the pancrease is shown in Figure 10.11.
10.5.2 Finding pancreas
10.5.3 Tips
Pancrease is best examined in fasted patient.
If bowel gas obstruct the view, try:
Examine after the patient change position:
- From lateral decubitus to supine, or
- From supine to upright (sit).
Use acoustic windows:
Let the patient drink some water to fill in the stomach.
View through the liver.